Entra ID SAML (formerly Azure AD)
Learn how to configure a connection to Entra ID via SAML.
Each SSO Identity Provider requires specific information to create and configure a new Connection. And often, the information required to create a Connection will differ by Identity Provider.
To create an Entra ID SAML Connection, you’ll need the Identity Provider Metadata URL that is available from the organization’s Entra ID instance.
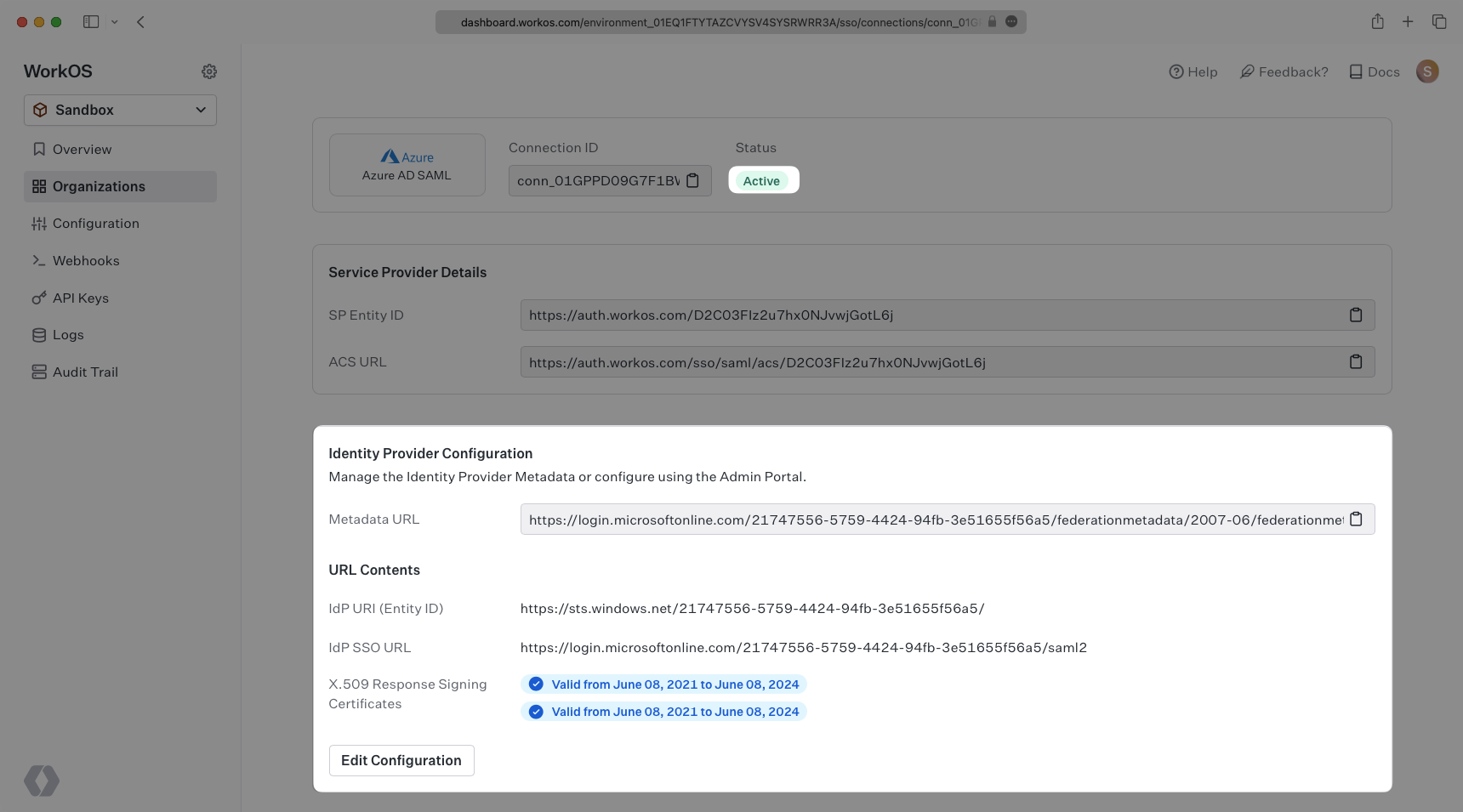
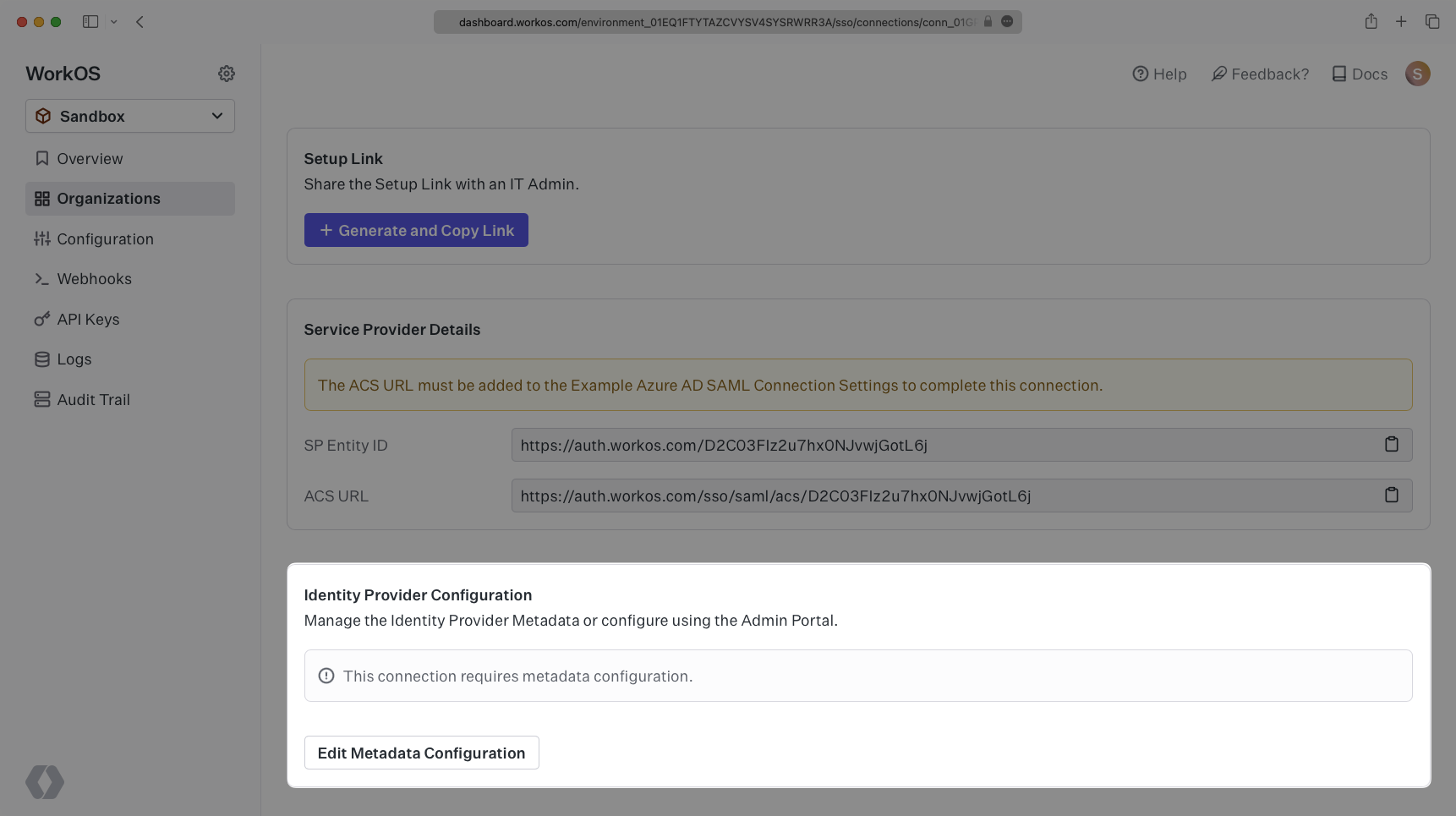
WorkOS provides the ACS URL and IdP URI (Entity ID). It’s readily available in your Connection Settings in the WorkOS Dashboard.
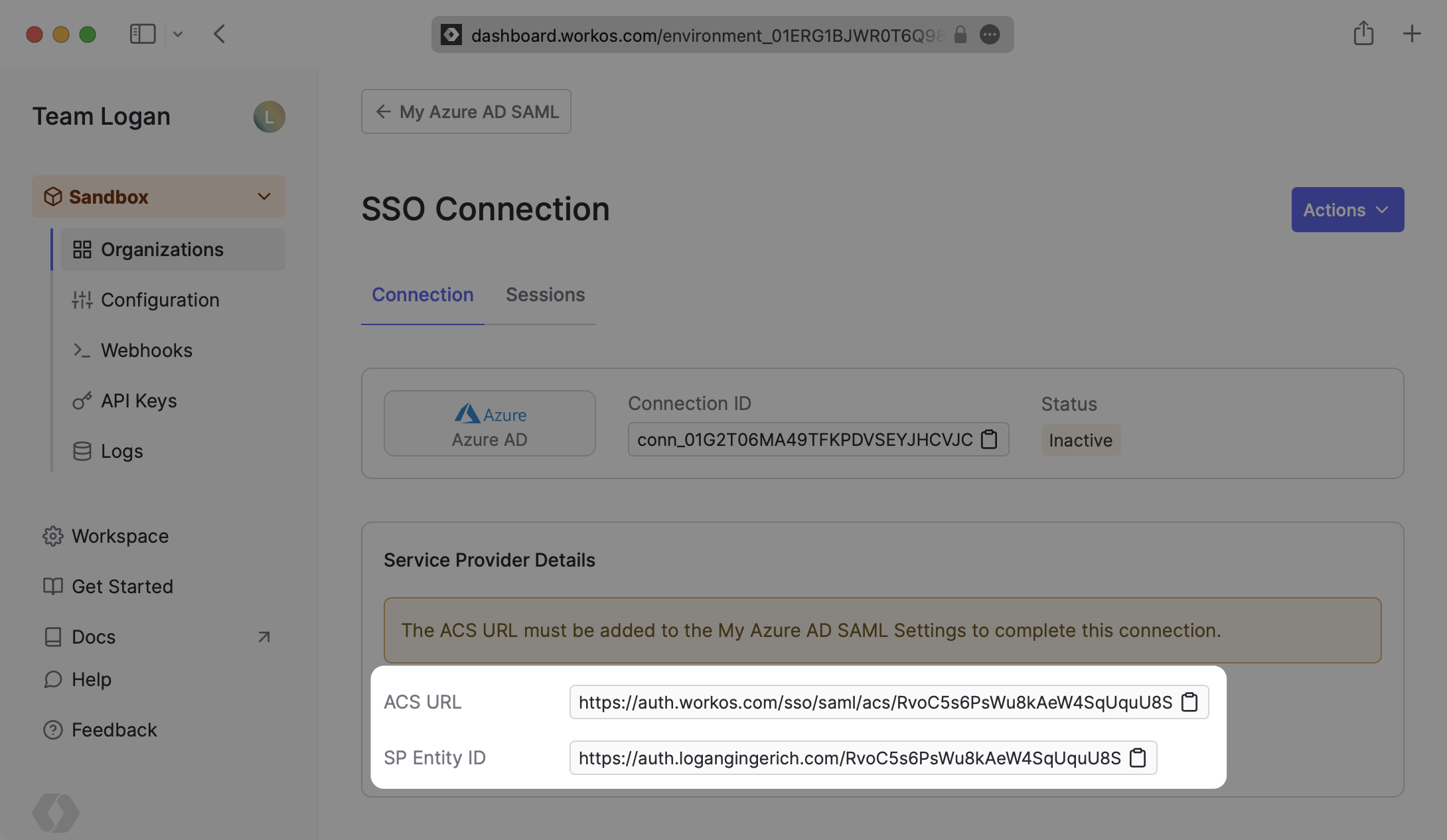
The ACS URL is the location an Identity Provider redirects its authentication response to. In Entra ID’s case, it needs to be set by the organization when configuring your application in their Entra ID instance.
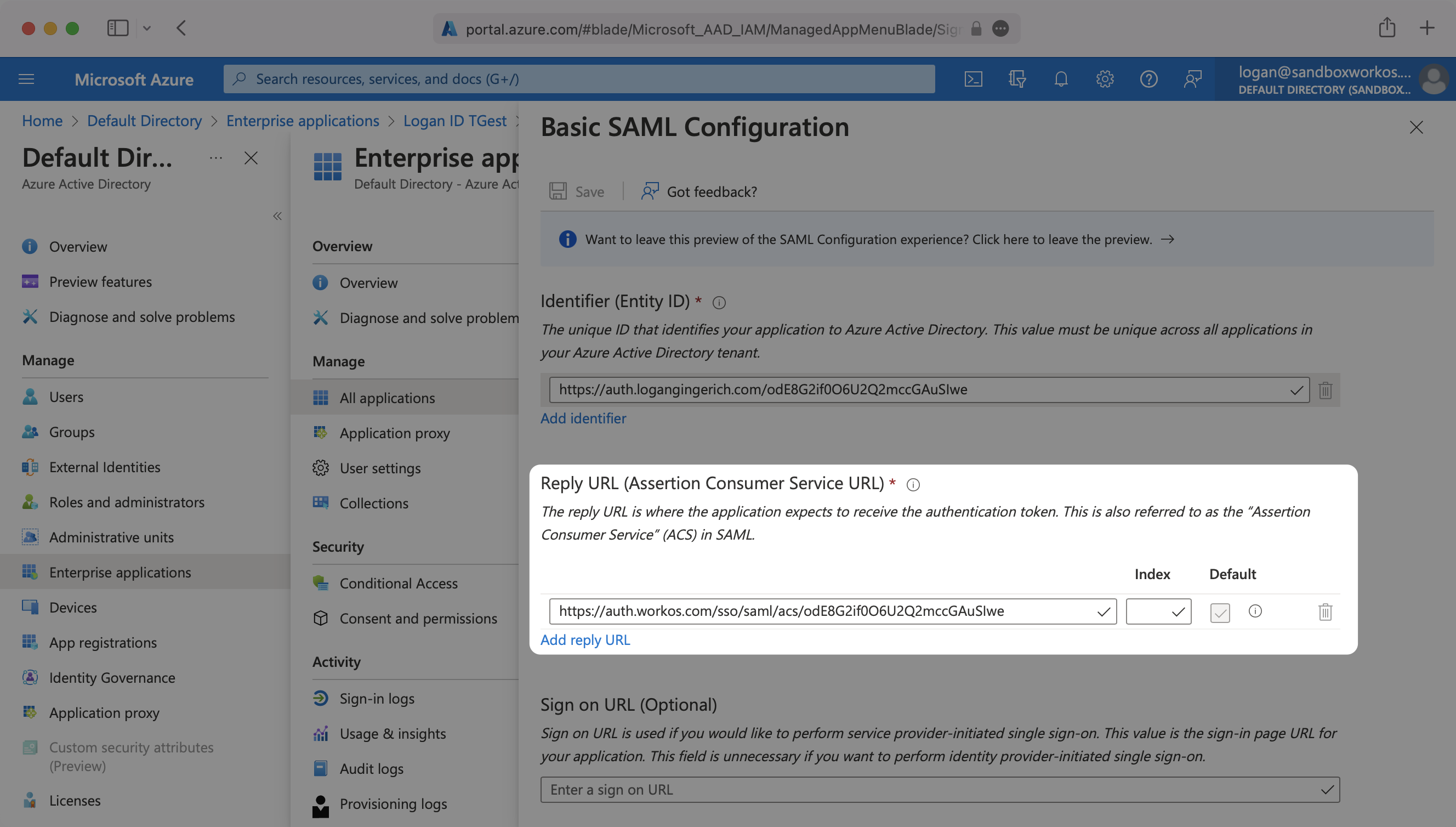
Specifically, the ACS URL will need to be set as the “Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL)” in the “Basic SAML Configuration” step of the Entra ID “Set up Single Sign-On with SAML” wizard:
The Entity ID is a URI used to identify the issuer of a SAML request, response, or assertion. In this case, the entity ID is used to communicate that WorkOS will be the party performing SAML requests to the organization’s Entra ID instance.
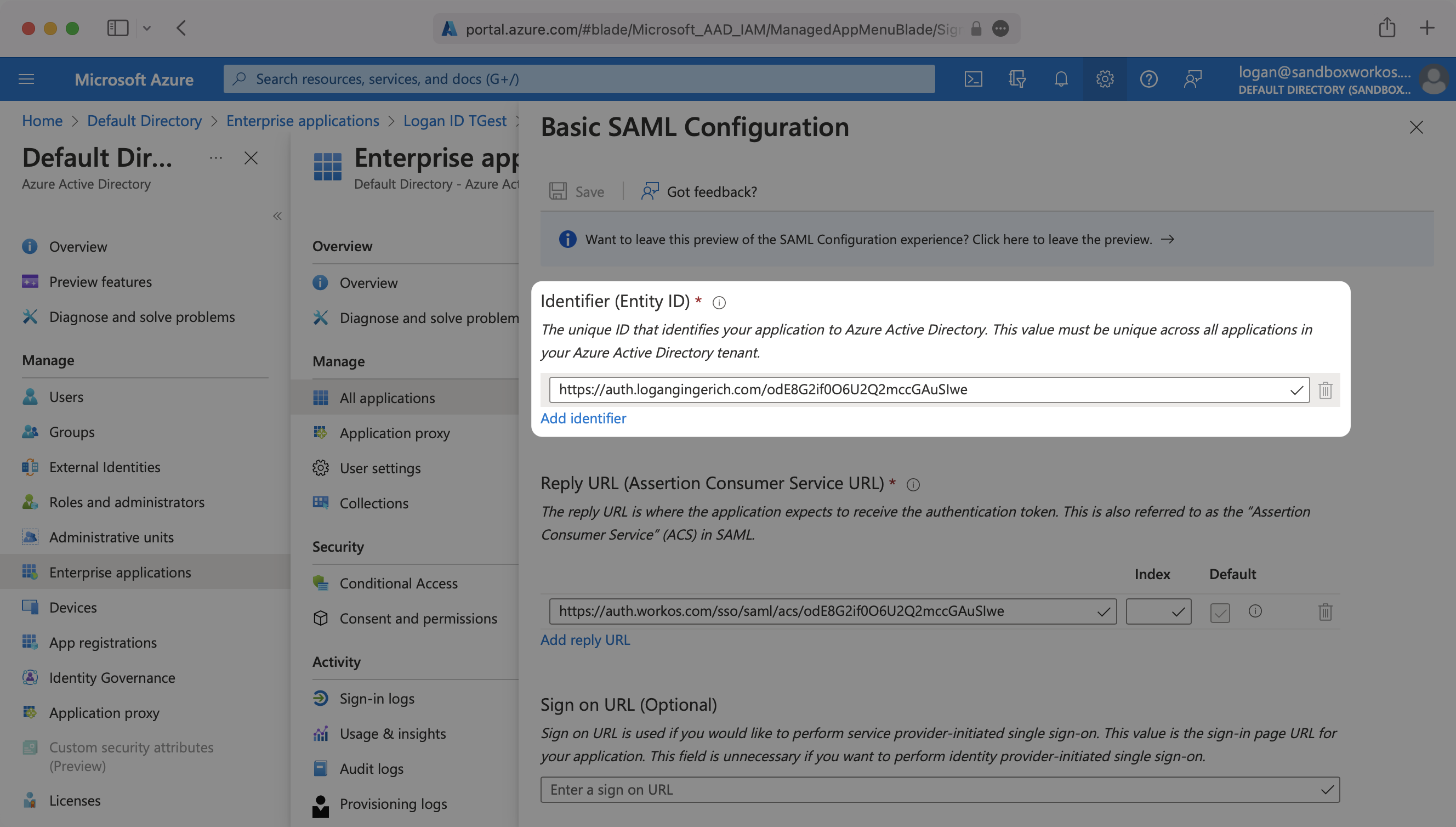
Specifically, the Entity ID will need to be set as the “Identifier (Entity ID)” in the “Basic SAML Configuration” step of the Entra ID “Set up Single Sign-On with SAML” wizard:
In order to integrate you’ll need the Entra ID IdP Metadata URL.
Normally, this information will come from the organization’s IT Management team when they set up your application’s SAML 2.0 configuration in their Azure admin dashboard. Here’s how to obtain them:
Log in to the Entra ID Active Directory Admin dashboard. Select “Enterprise Applications” from the list of Azure services.
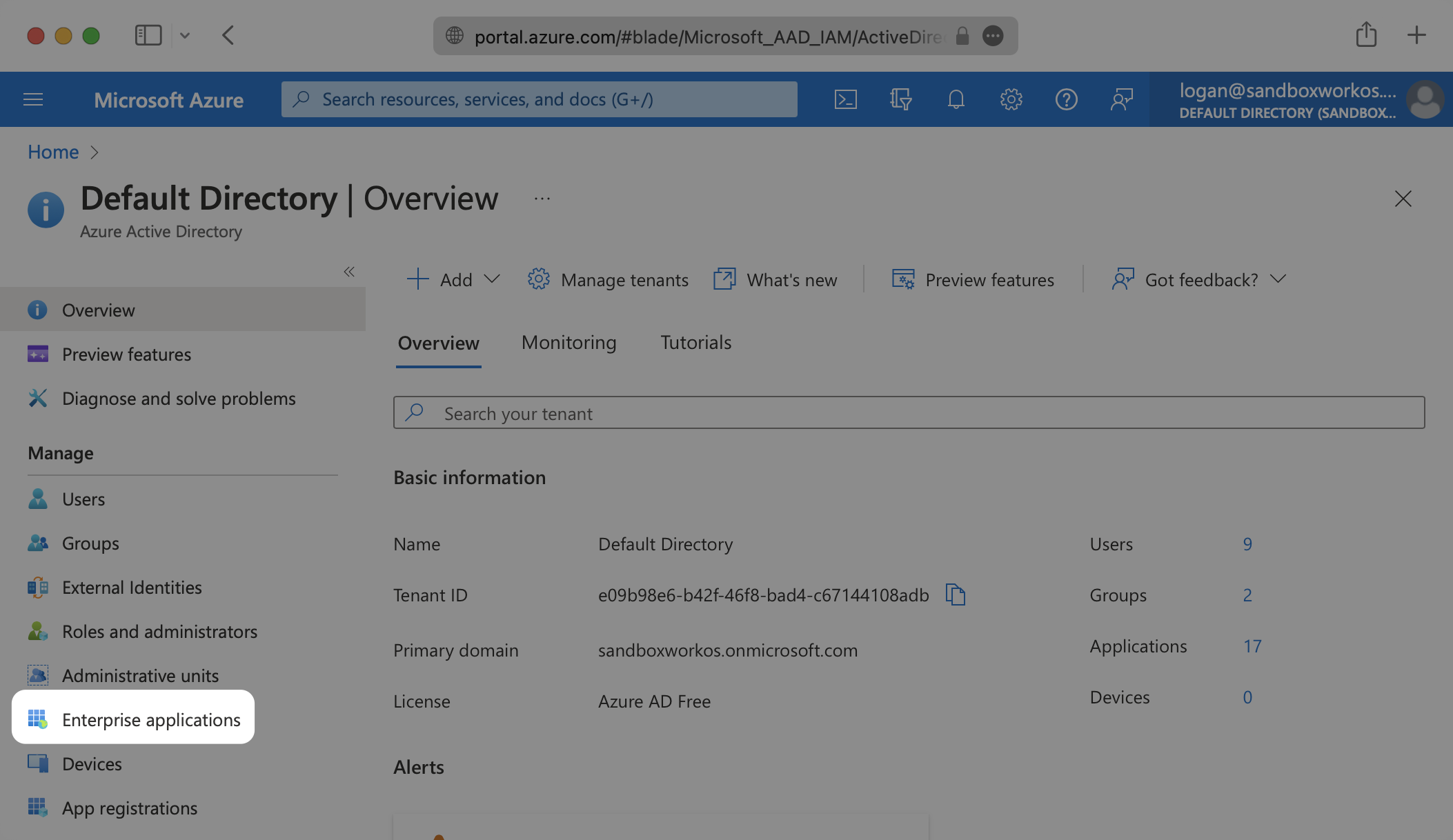
If your application is already created, select it from the list of Enterprise applications and move to Step 7.
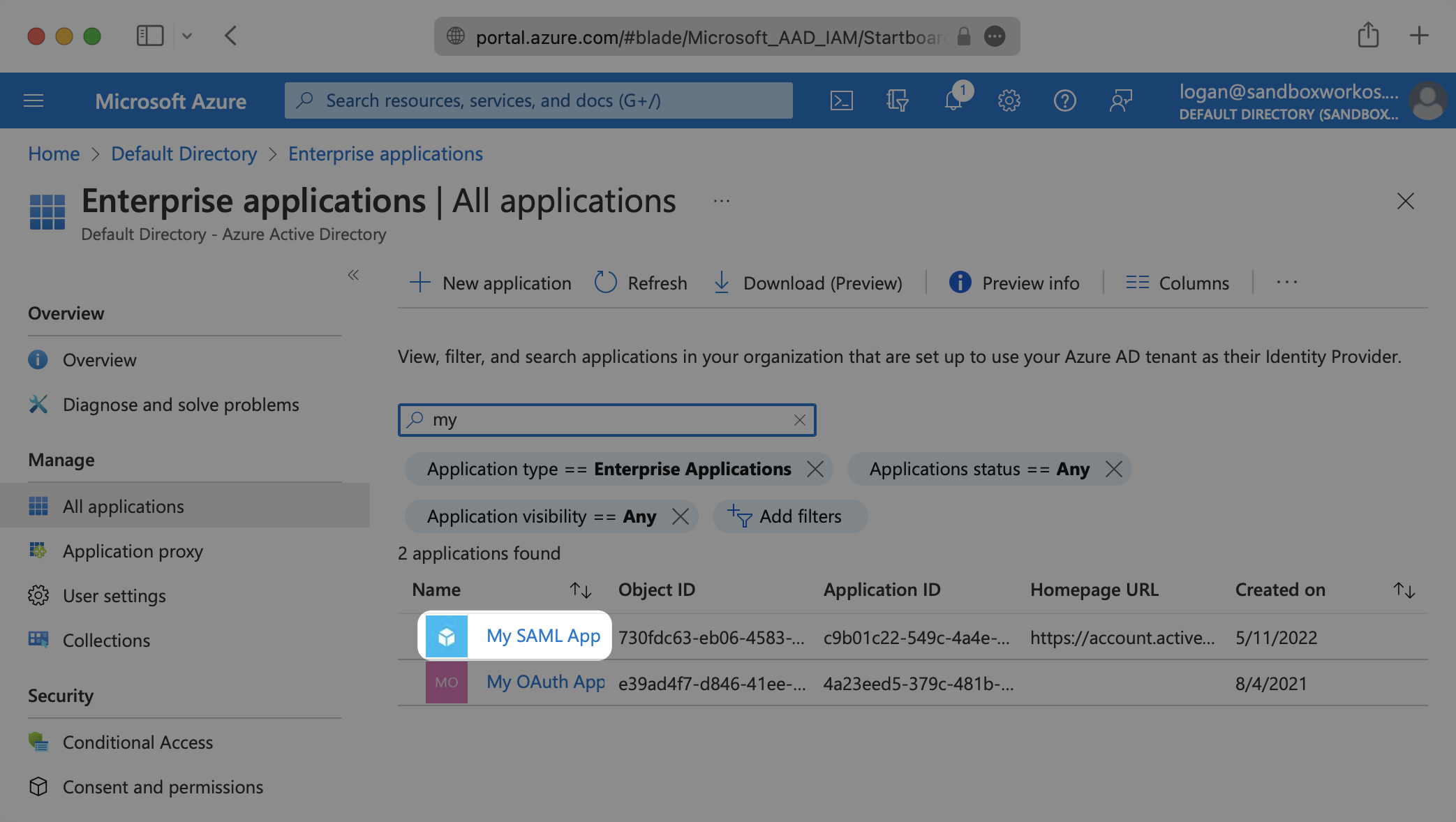
If you haven’t created a SAML Application in Azure, select “New Application”.
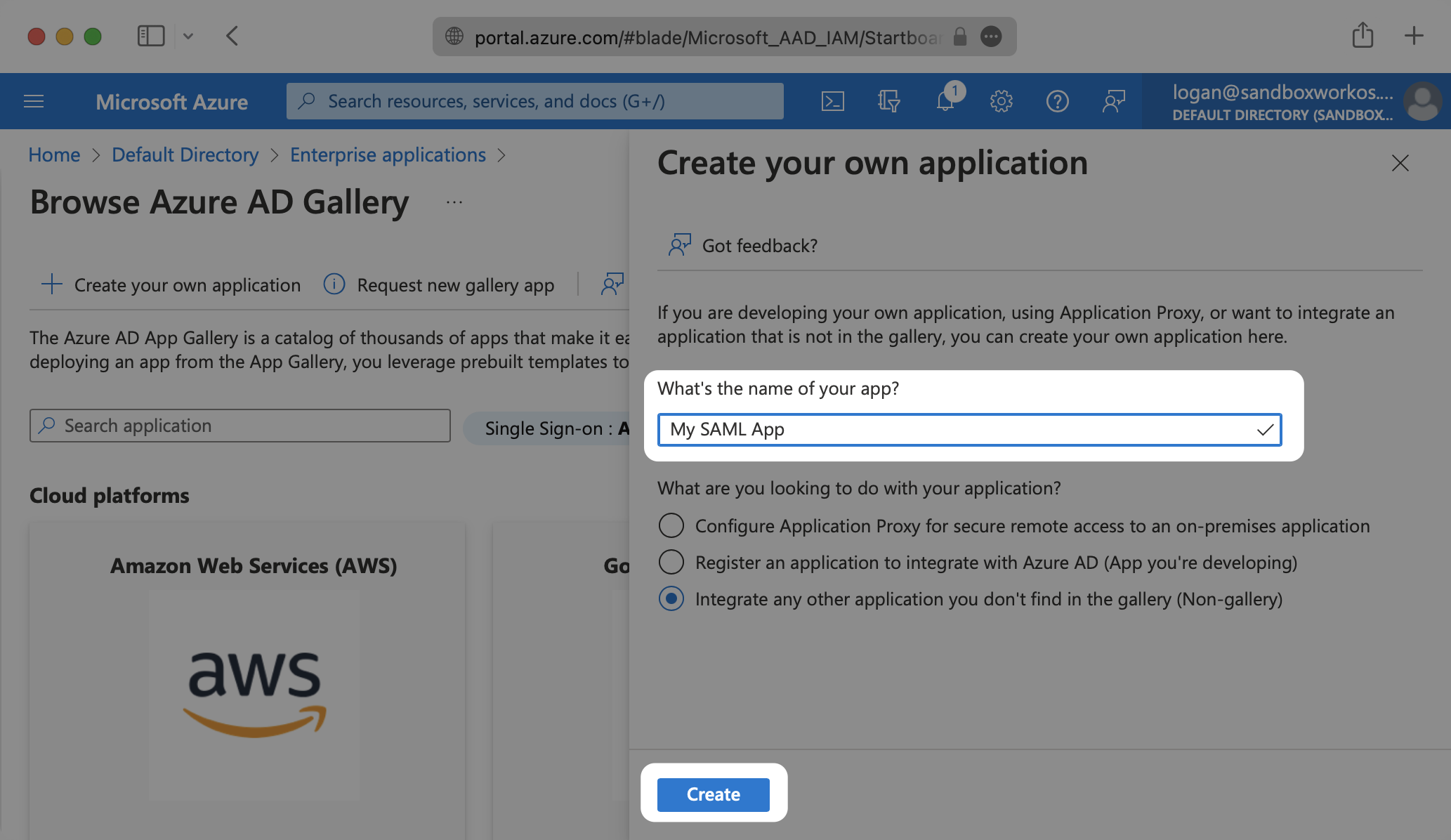
Select “Create your own application”, then enter a descriptive app name. Under “What are you looking to do with your application?”, select “Integrate any other application you don’t find in the gallery (Non-gallery)”, then select “Create”.
Select “Single Sign-On” from the “Manage” section in the left sidebar navigation menu, and then “SAML”.
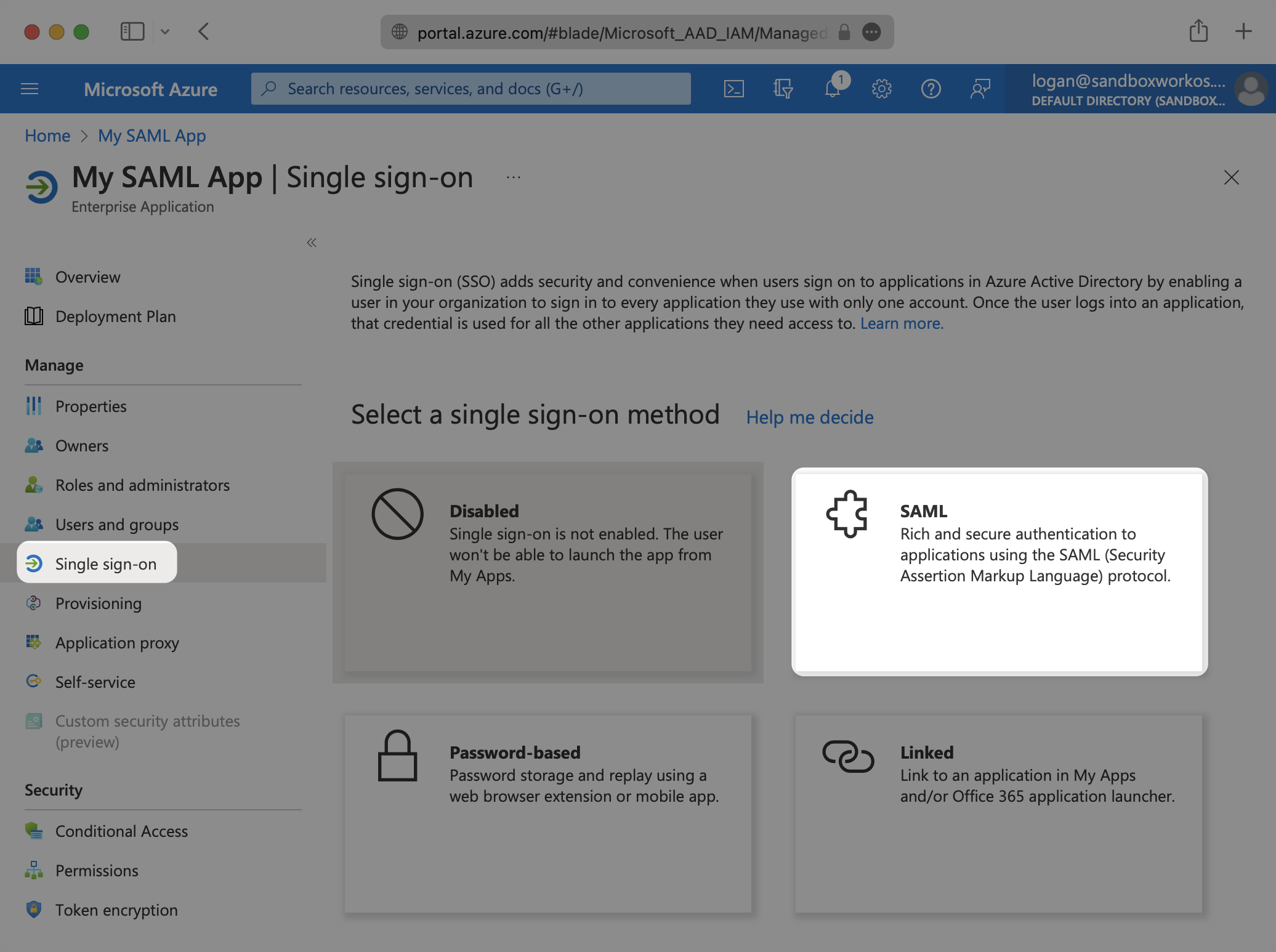
Click the Edit icon in the top right corner of the first step “Basic SAML Configuration”.
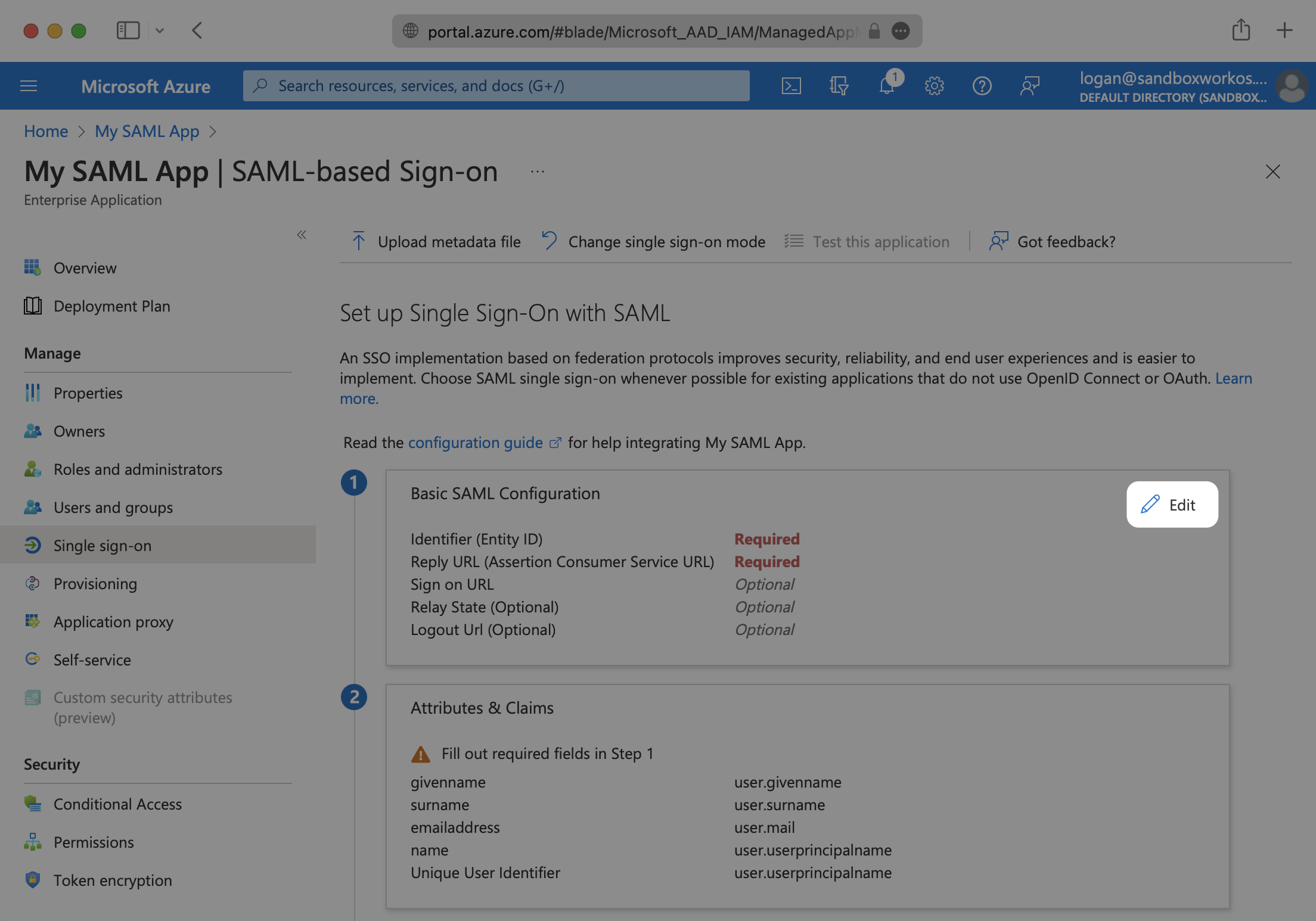
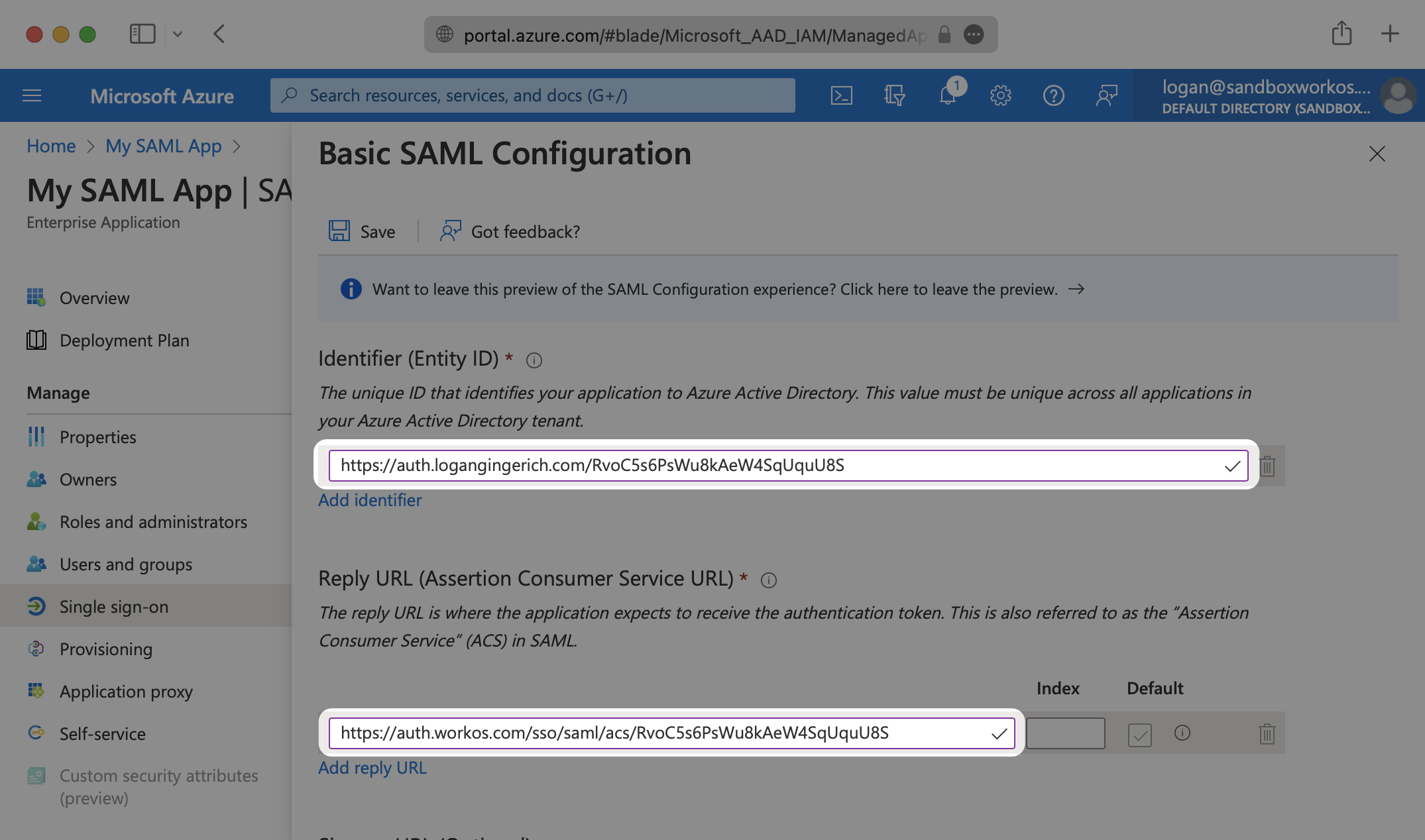
Input the IdP URI (Entity ID) from your WorkOS Dashboard as the “Identifier (Entity ID)”. Input the ACS URL from your WorkOS Dashboard as the “Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL)”.
Click the Edit icon in the top right corner of the second step “Attributes & Claims”.
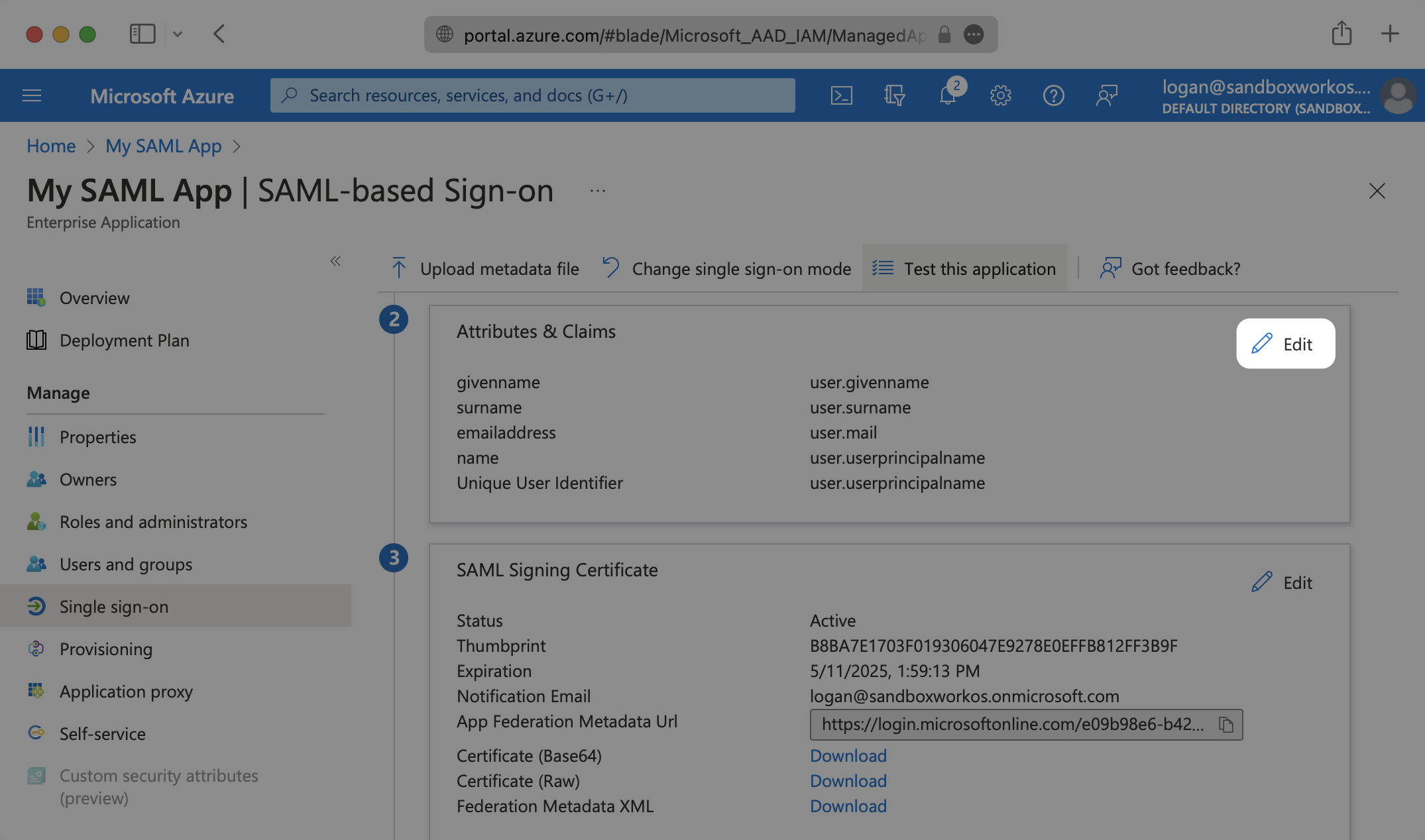
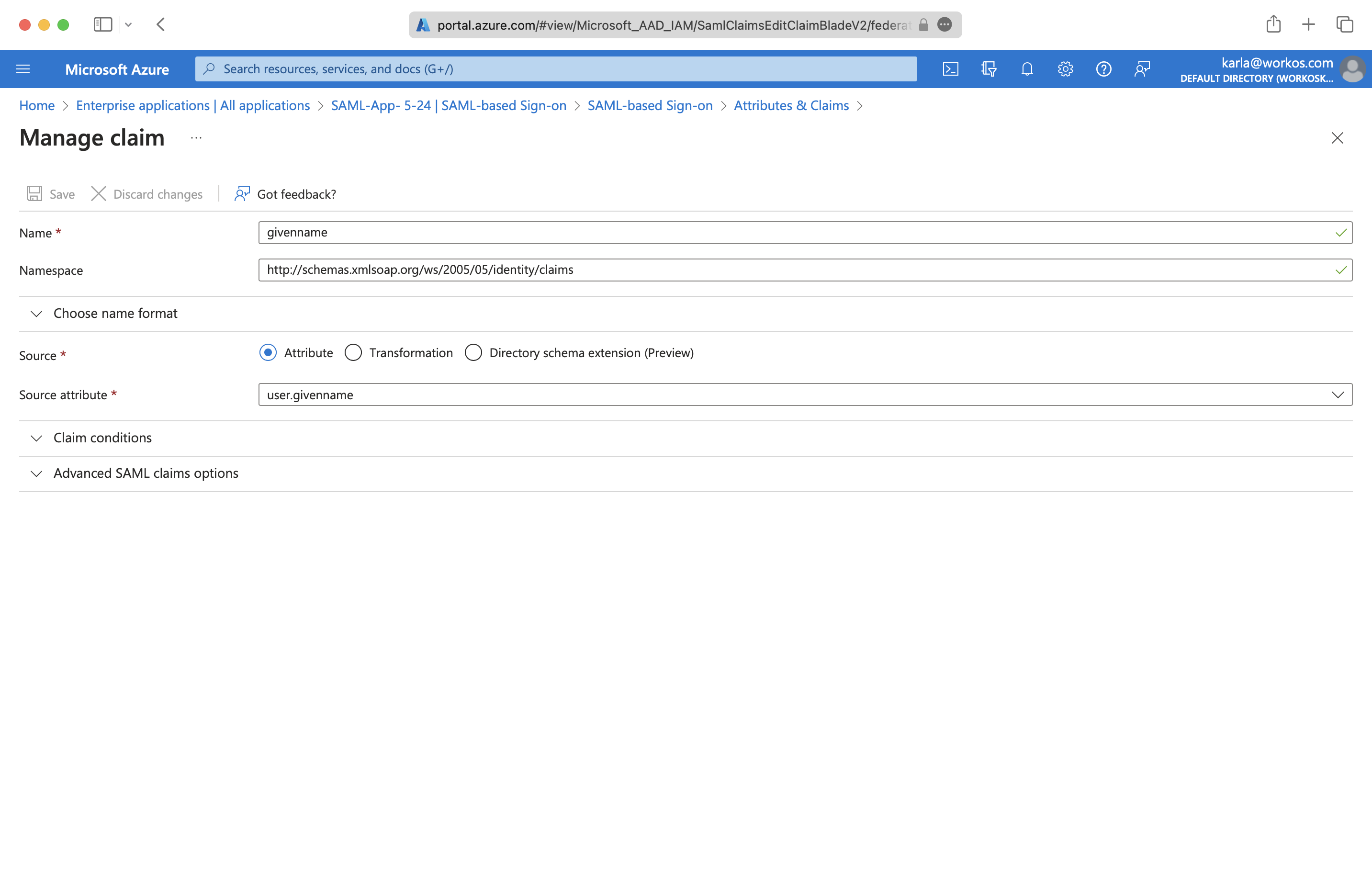
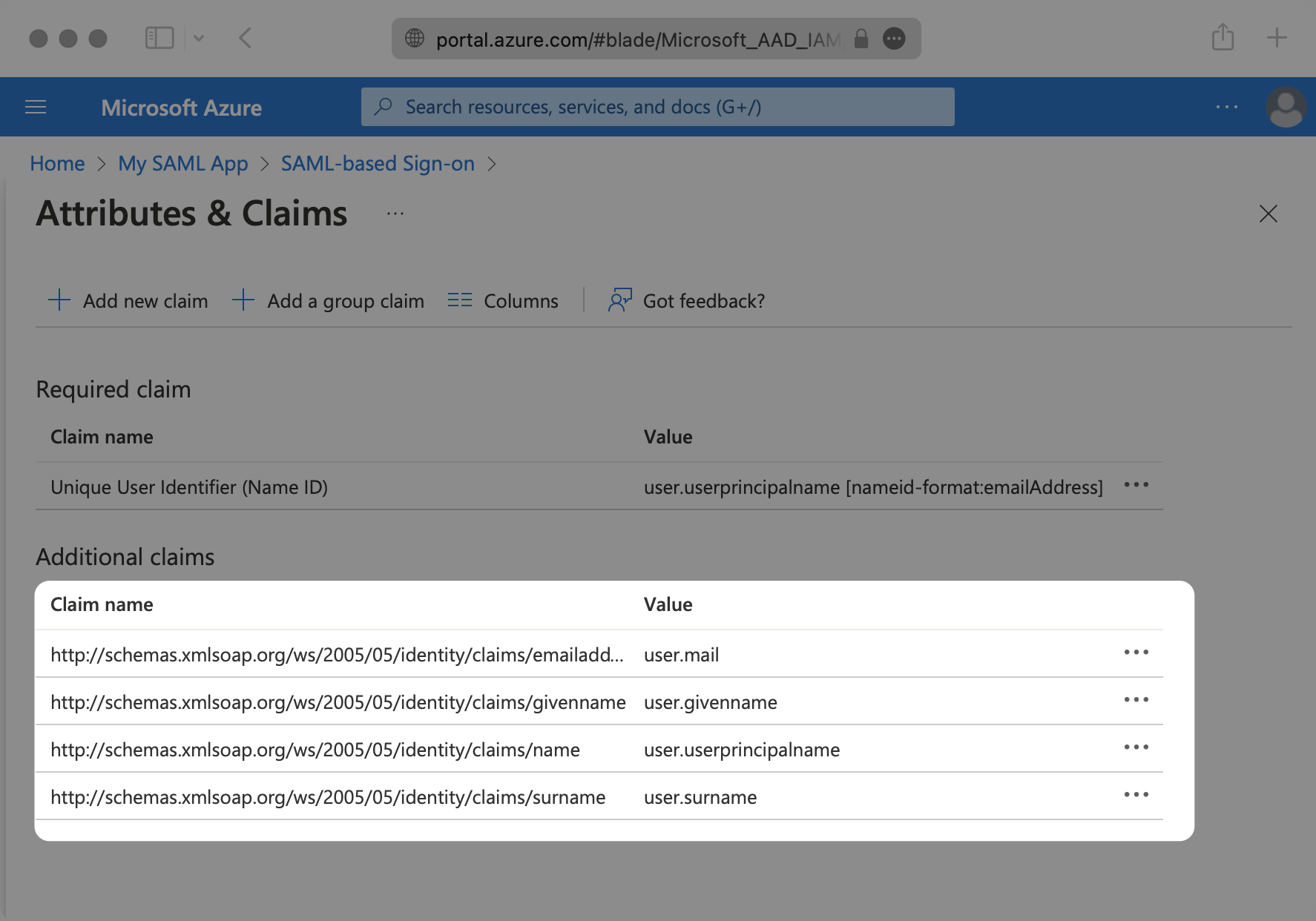
Make sure the following attribute mapping is set:
http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/emailaddress→user.mailhttp://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/givenname→user.givennamehttp://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/name→user.userprincipalnamehttp://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/surname→user.surname
Below is an example of how to format your claim within the Azure claim editor. Make sure the ‘Namespace’ value ends in /claims.
With identity provider role assignment, users can receive roles within your application based on their group memberships. To return this information in the attribute statement, follow the guidance below.
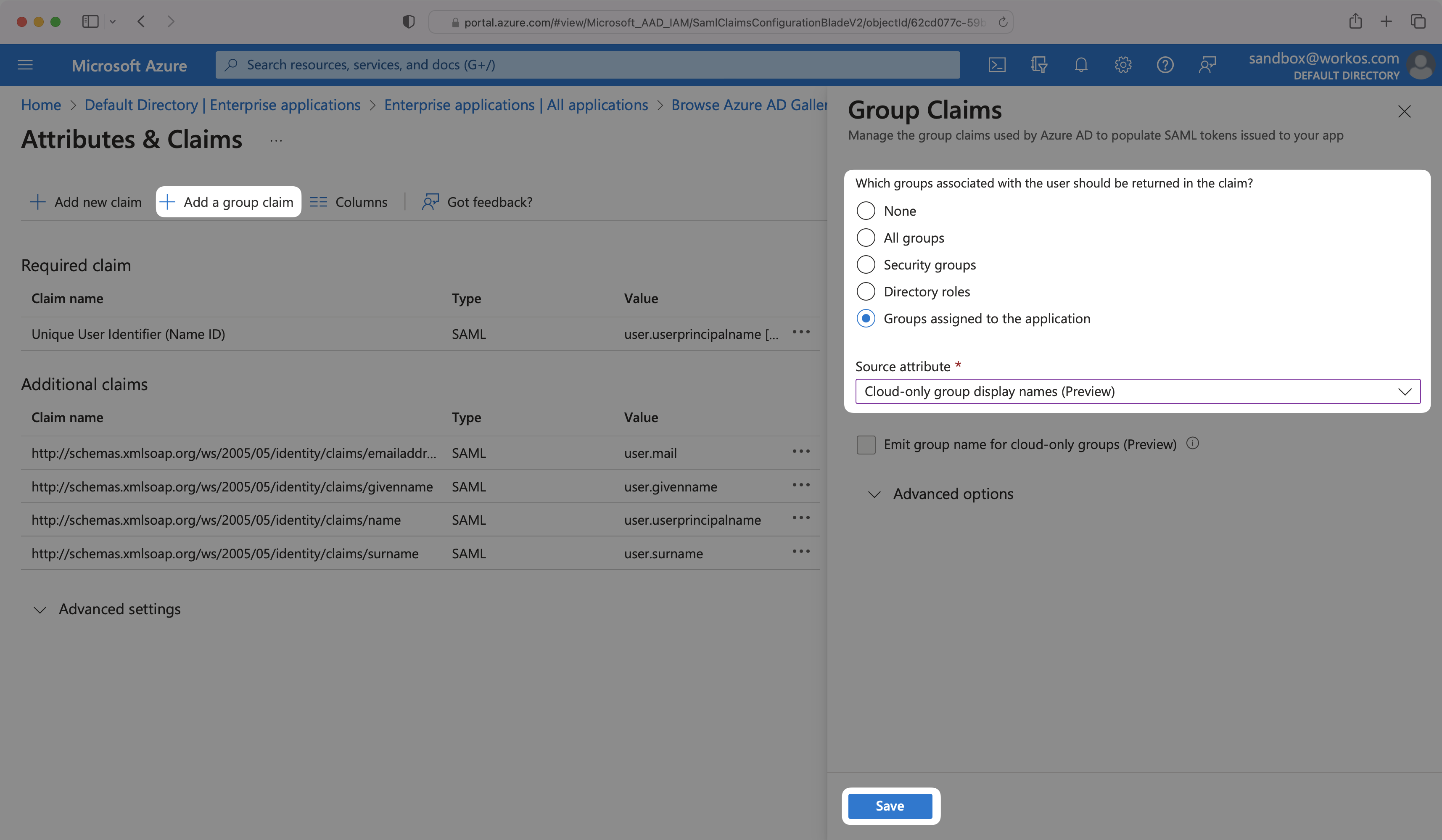
Select “Add a group claim” from the top menu. Next, select which groups you’d like to return in the Group Claims settings. For example, in Entra ID, you could select “Groups assigned to the application” to only send groups assigned to the SAML app. Finally, select “Save” once finished configuring the groups.
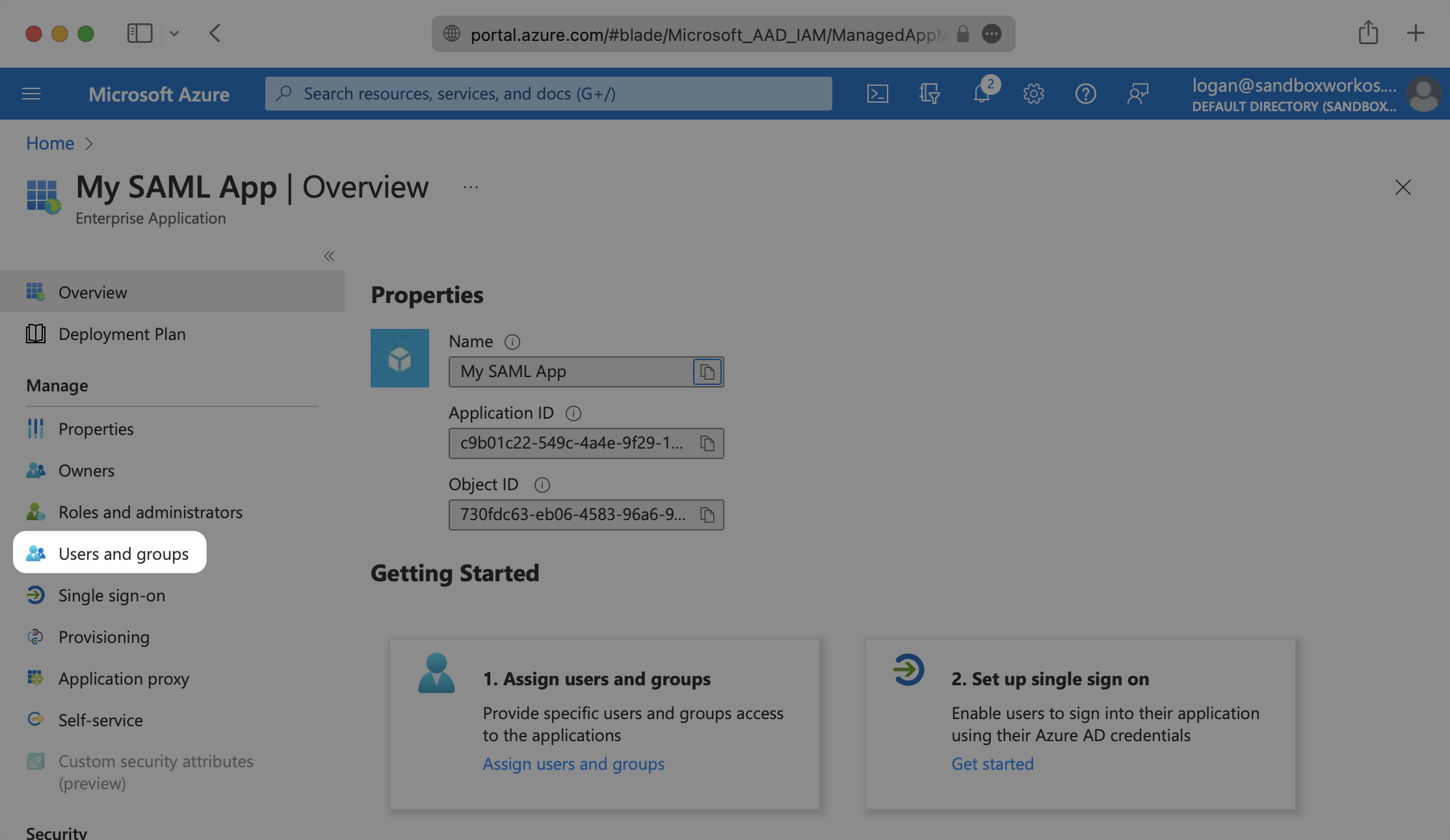
In order for your users or groups of users to be authenticated, you will need to assign them to your Entra ID SAML application. Select “Users and groups” from the “Manage” section of the navigation menu.
Select “Add user/group” from the top menu.
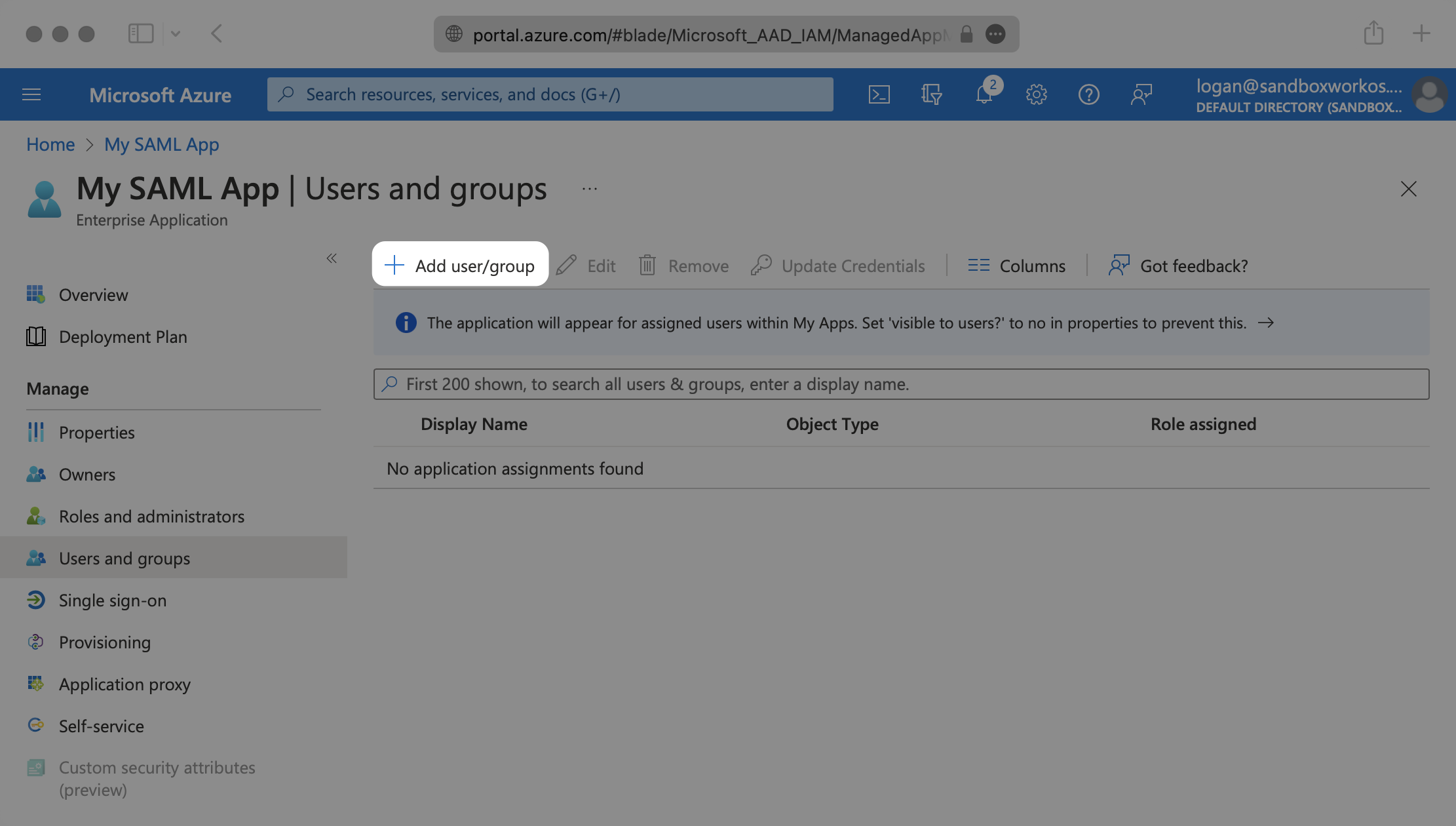
Select “None selected” under the “Users and Groups”. In the menu, select the users and groups of users that you want to add to the SAML application, and click “Select”.
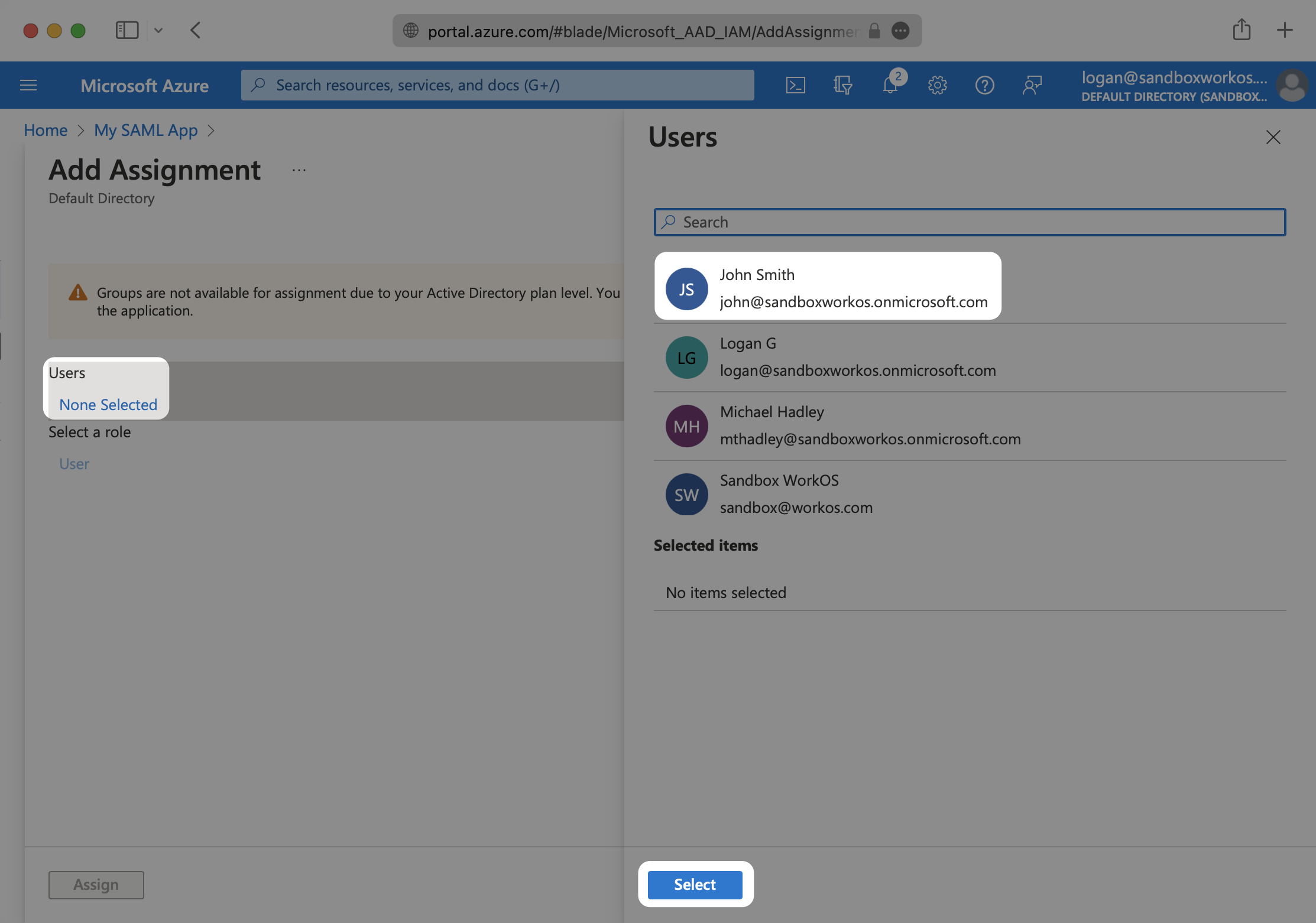
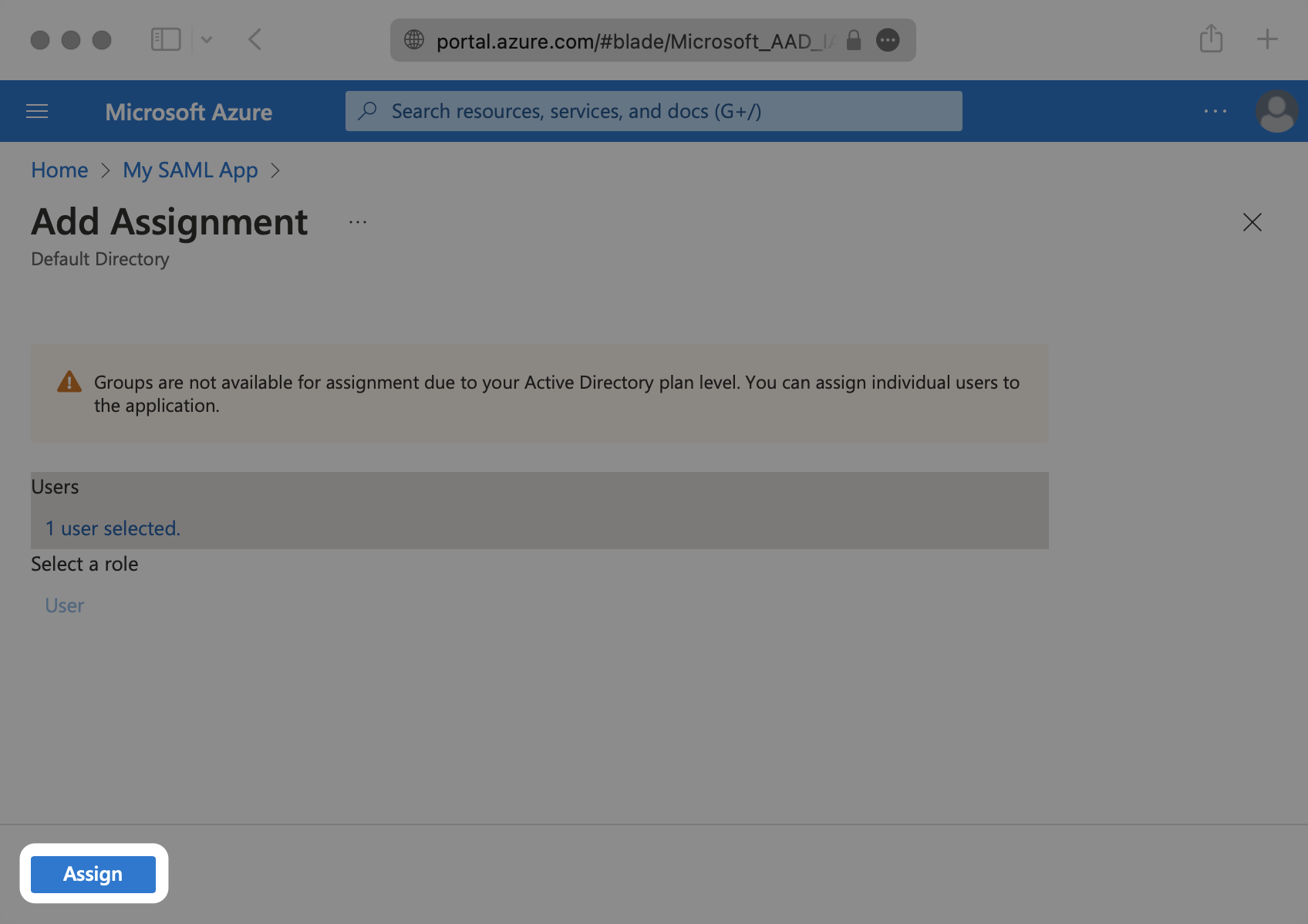
Select “Assign” to add the selected users and groups of users to your SAML application.
Select “Single Sign-On” from the “Manage” section in the left sidebar navigation menu.
Navigate down to Section 3 of the “Single Sign-On” page, to “SAML Signing Certificate”. Copy the URL provided in “App Federation Metadata URL”.
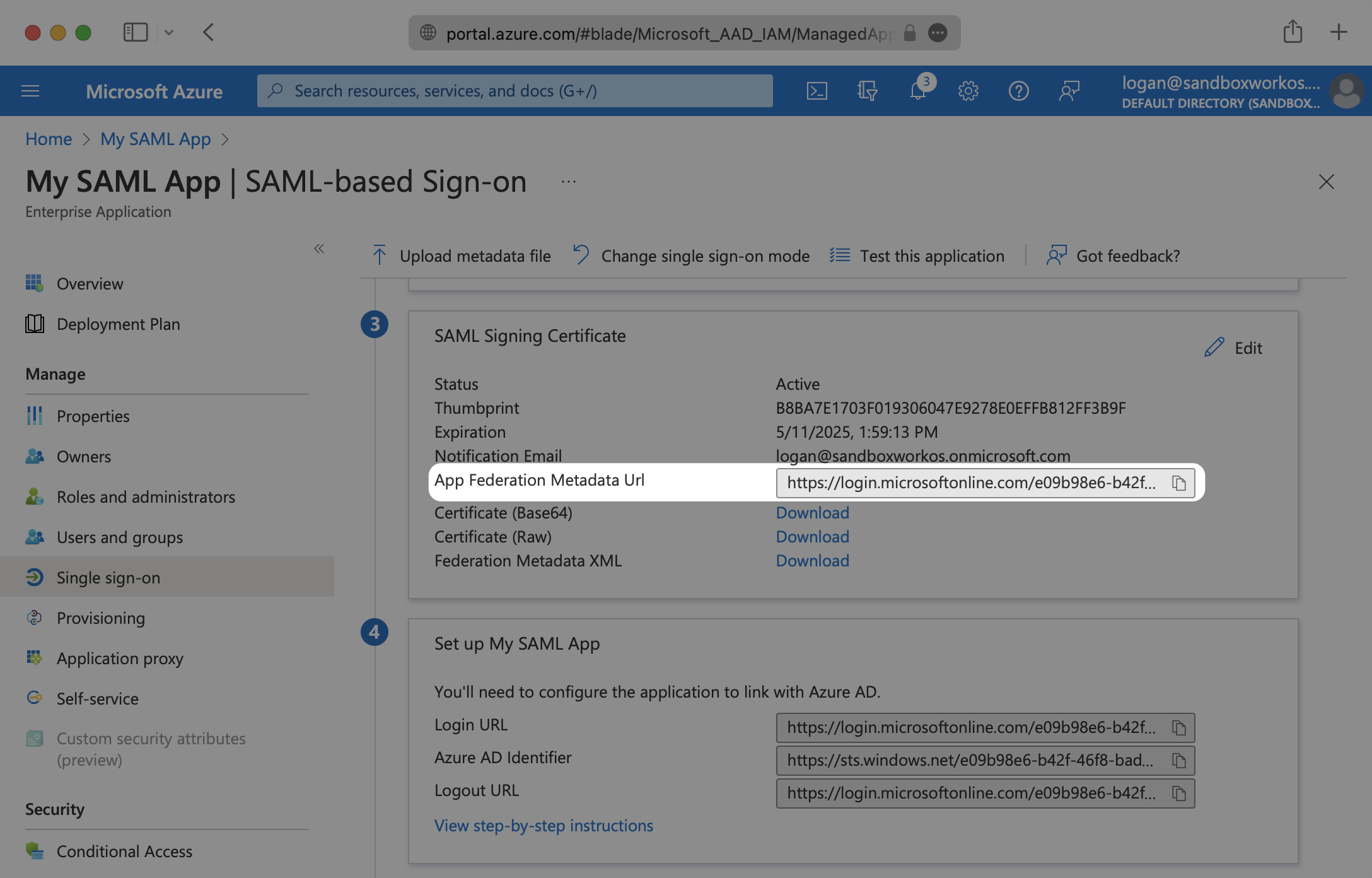
Next, within your connection settings under “Identity Provider Configuration”, select “Edit Metadata Configuration” and enter the Azure metadata URL.
Your Connection will then be verified and good to go!