Handle Inactive Users
Learn why inactive users are deleted from directories by default and how to configure this behavior.
Traditionally, user provisioning involves the ingestion of user information from various providers (either through SCIM or non-SCIM integrations). This process typically includes categorizing users into states such as active, or inactive as provided by the IdP data source.
However, the challenge arises when businesses need to handle these inactive users differently based on their unique operational and security requirements. Some developers may prefer a security-first approach, automatically deleting these users to enhance data security, while others may opt to retain this information for reactivation processes or comprehensive directory management.
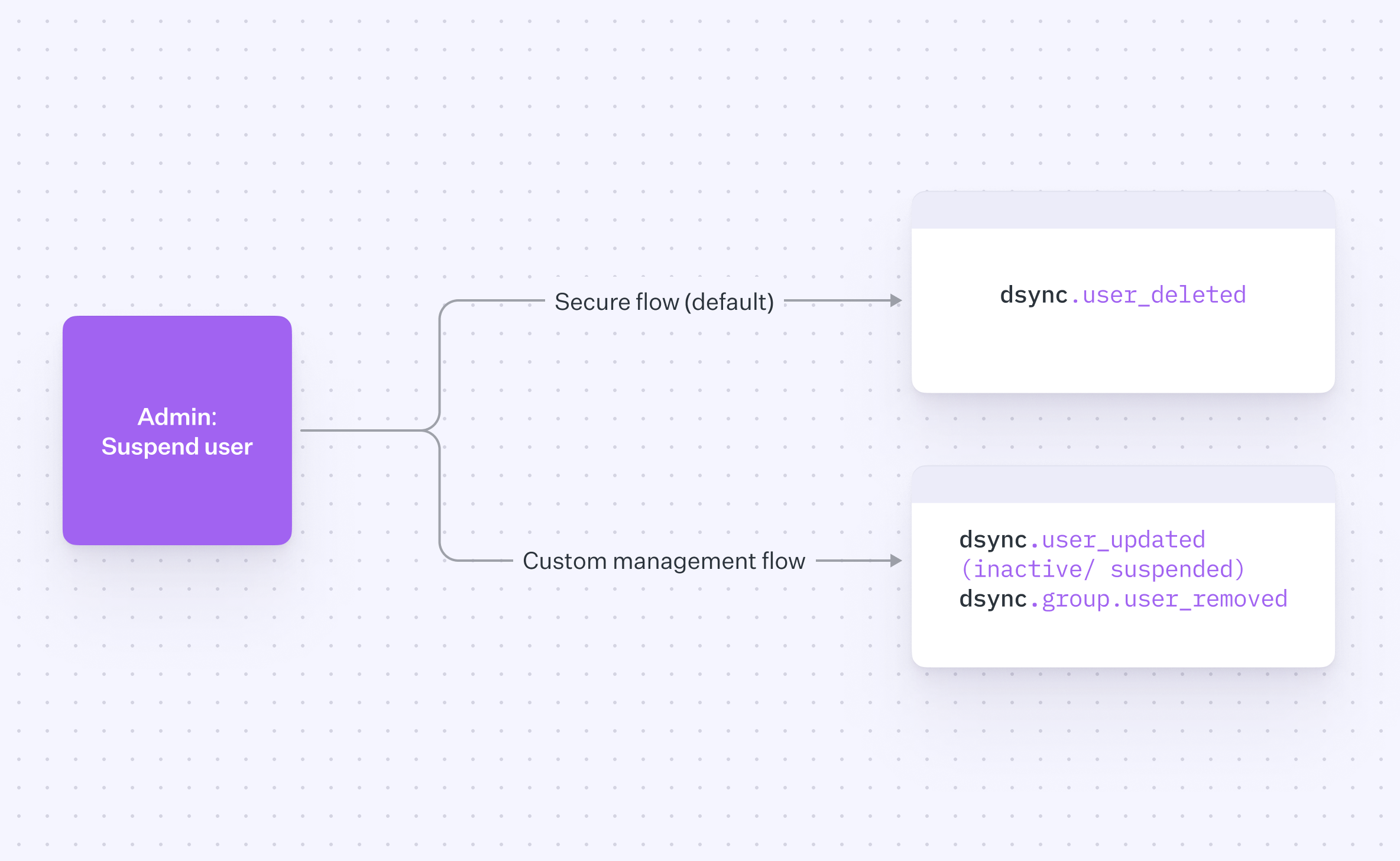
To provide improved security and customizability, you can choose how inactive users are handled during the provisioning process. Here is an overview of the two options available:
By selecting this option, customers can opt for a security-focused workflow. Any user marked as inactive will be automatically deleted from the directory, resulting in cleaner and potentially more secure data. This approach reduces the data footprint and minimizes potential security risks associated with unused accounts.
Alternatively, customers can choose to maintain the existing flow, keeping the inactive users in the directory. This approach supports reactivation processes and ensures a comprehensive view of the directory, allowing for easier reintegration of users when needed.
Contact customer support to enable custom management flow for your environment.
Both options offer distinct advantages, and the right choice depends on your organization’s unique needs and security posture:
The automatic deletion option prioritizes data security by minimizing the data footprint, while the customized management option provides flexibility for reactivation flows and comprehensive directory oversight.
Depending on industry regulations and compliance requirements, one option may align better with your organization’s obligations.
Consider how each option impacts operational efficiency using WorkOS to handle a set of the computation for you.